Cyclic Changes (HS-ESS1-7): Construct an explanation using evidence to support the claim that the phases of the moon, eclipses, tides and seasons change cyclically
Constructing an explanation using evidence shows that the phases of the moon, eclipses, tides, and seasons change in a predictable, cyclic manner. The moon's phases result from its orbit around Earth, causing it to appear differently from our viewpoint. Eclipses occur in predictable cycles due to the alignment of the Earth, moon, and sun. Tides follow a regular pattern driven by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. Seasonal changes are caused by Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun, leading to variations in sunlight and temperature throughout the year. This cyclical behavior is supported by observational evidence and astronomical principles.
Main Concepts:
- Phases of the Moon: The moon goes through eight distinct phases that repeat in a cyclic pattern. These phases are caused by the changing positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun relative to each other. As the Moon orbits around Earth, the amount of sunlight that reflects off its surface changes, creating the different phases. The eight phases are: new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent.
- Eclipses: There are two types of eclipses, solar and lunar, which occur when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned in a specific way. Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun's light and casting a shadow on Earth. Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon and causing it to appear red or orange.
- Tides: Tides are the rise and fall of Earth's ocean waters caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun create a tidal bulge on the side of Earth closest to them, which causes a high tide. The opposite side of Earth experiences a high tide as well due to the centrifugal force created by the Earth's rotation. The areas in between experience a low tide. The tides change cyclically because of the changing positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun relative to each other.
- Seasons: The changing seasons on Earth are caused by the Earth's tilt on its axis. The Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt causes the amount of sunlight that reaches different parts of the Earth to vary throughout the year. When a hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it receives more direct sunlight and experiences summer. When it is tilted away from the Sun, it receives less direct sunlight and experiences winter. The two solstices occur when the tilt is at its maximum and the equinoxes occur when the tilt is at its minimum.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
The Effect of the Moon on Earth: Earth’s Moon is the only celestial object beyond Earth where humans have set foot. It is the brightest and largest object in the night sky. The Moon makes Earth a more livable planet by moderating the wobble of Earth on its axis, leading to a relatively stable climate. The models below represent two different positions of a person on Earth’s surface six hours apart. The relative height of the ocean tides at these positions are indicated. The arrow represents the direction of Earth’s rotation.
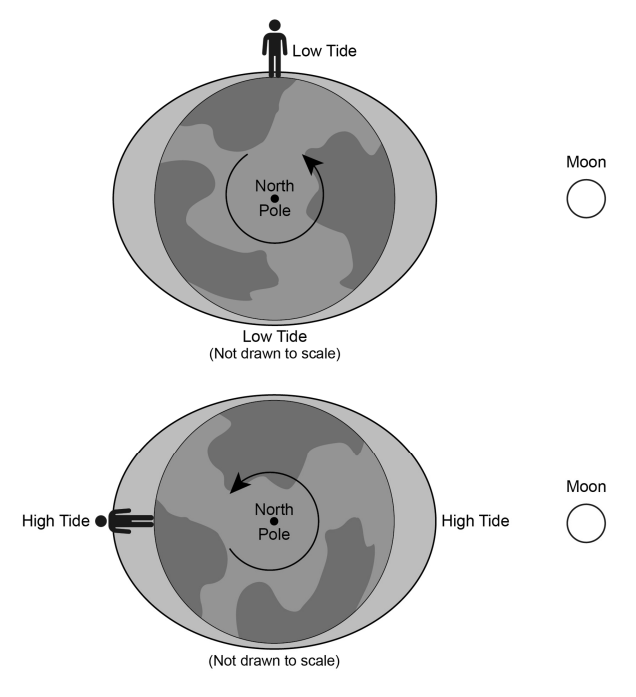
| Construct an explanation using evidence from the models to support the claim that tides on Earth change cyclically. | |
|---|---|
— Every six hours the observer experiences a different tide height from low to high or high to low because of Earth’s regular rotation every 24 hours.
— In a 24-hour period, the person experiences two high tides and two low tides.
General Question and Answer Section:
- What causes the different phases of the moon?
Answer: The changing positions of the moon, Earth, and Sun relative to each other cause the different phases of the moon. - How many distinct phases of the moon are there?
Answer: There are eight distinct phases of the moon. - What are the two types of eclipses?
Answer: The two types of eclipses are solar and lunar. - What causes tides on Earth?
Answer: Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the Sun on the Earth's water bodies. - Why do the tides change cyclically?
Answer: The tides change cyclically because of the changing positions of the moon, Earth, and Sun relative to each other. - What causes the changing seasons on Earth?
Answer: The changing seasons on Earth are caused by the Earth's tilt on its axis. - How many degrees is the Earth's tilt on its axis?
Answer: The Earth's tilt on its axis is 23.5 degrees. - What is a solar eclipse?
Answer: A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the Sun and Earth. - What is a lunar eclipse?
Answer: A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and moon. - Why do eclipses occur cyclically?
Answer: Eclipses occur cyclically because the Sun, Earth, and moon align in a specific way during certain times of the year.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
Space Systems: HS-ESS1-1 : HS-ESS1-2 : HS-ESS1-3 : HS-ESS1-4 : HS-ESS1-7
History of the Earth: HS-ESS1-5 : HS-ESS1-6 : HS-ESS2-1
Earth's Systems: HS-ESS2-2 : HS-ESS2-3 : HS-ESS2-5 : HS-ESS2-6 : HS-ESS2-7
Weather and Climate: HS-ESS2-4 : HS-ESS3-5 : HS-ESS2-8
Human Sustainability: HS-ESS3-1 : HS-ESS3-2 : HS-ESS3-3 : HS-ESS3-4 : HS.ESS3-6
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Earth and Space Science assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.