Energy Variation and Climate Change (HS-ESS2-4): Use a model to describe how variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth's systems result in changes in climate.
Using a model to describe how variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth's systems illustrates how these changes affect climate. Fluctuations in energy input, such as changes in solar radiation or greenhouse gas concentrations, and energy output, including heat radiated back into space, can lead to alterations in Earth's climate. The model helps to show how these energy imbalances drive shifts in temperature, weather patterns, and overall climate conditions.
Main Concepts:
- Climate change is a term used to describe long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns that occur over several decades or longer. Scientists have been studying climate change for many years, and they have identified various factors that contribute to this phenomenon. One of the most important factors is the flow of energy into and out of Earth's systems, which can be influenced by many different things.
- Short-term changes in climate can be caused by volcanic eruptions or changes in solar radiation, while long-term changes can be caused by processes such as plate tectonic movement or variations in Earth's orbit. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation are also contributing to climate change by increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun and cause the Earth's temperature to rise.
- Models are used to understand the complex relationships between Earth's systems and how they contribute to climate change. These models incorporate data from many different sources, including atmospheric measurements, oceanic measurements, and ice core records. By simulating the interactions between these systems, scientists can gain insights into the processes that contribute to climate change and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
- In addition to its impact on the natural environment, climate change also has significant implications for human societies. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to changes in agricultural productivity, water availability, and disease prevalence. Rising sea levels, more frequent heat waves and extreme weather events, and changes in the distribution of plant and animal species are all examples of the many ways in which climate change is affecting the world we live in.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
Earth’s Climate: Earth’s climate is the result of energy interacting with the substances and surfaces that make up Earth’s spheres. While Earth’s spheres have different properties and characteristics, they are not isolated from each other. Interactions between these spheres have caused feedbacks that have changed Earth’s climate over decades. The model below shows information about the Arctic climate.
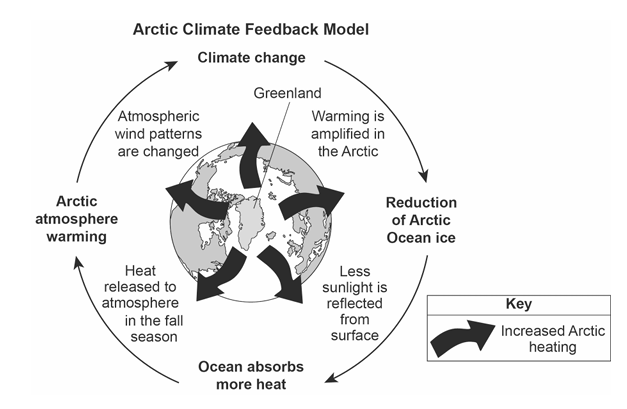
| Use evidence from the climate model to describe how a reduction of Arctic Ocean ice will cause a change in average atmospheric pressures above the Arctic Ocean, and how this change in pressure results in a change of climate. | |
|---|---|
— Heat released by the warming ocean will enter into the atmosphere, lowering atmospheric pressure and causing the Arctic region to warm.
— Increased Arctic heating will reduce the amount of sea ice and expose more ocean water to absorb heat, which enters the atmosphere, lowering average air pressure by adding moisture to the atmosphere and warming the climate
Question and Answer Section:
- What is climate change? A: Climate change refers to the long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
- How do variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth's systems affect climate? A: Variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth's systems can result in changes in climate.
- What are some causes of climate change on a short-term timescale? A: Some causes of climate change on a short-term timescale include large volcanic eruptions and changes in ocean circulation.
- What are some causes of climate change on a long-term timescale? A: Some causes of climate change on a long-term timescale include changes to Earth's orbit and the orientation of its axis, and long-term changes in atmospheric composition and plate tectonic movement.
- How can models be used to understand climate change? A: Models can be used to describe the complex relationships between the Earth's systems and how they contribute to climate change.
- Why is it important to understand the factors that contribute to climate change? A: It is important to understand the factors that contribute to climate change in order to mitigate its negative impacts.
- How do human activities contribute to climate change? A: Human activities contribute to climate change through the release of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.
- What are some potential impacts of climate change? A: Potential impacts of climate change include rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in ecosystems and the distribution of species.
- What is the difference between weather and climate? A: Weather refers to short-term changes in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns of weather in a particular area.
- What are some ways that individuals can help mitigate climate change? A: Individuals can help mitigate climate change by reducing their carbon footprint through actions such as driving less, using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing meat consumption.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
Space Systems: HS-ESS1-1 : HS-ESS1-2 : HS-ESS1-3 : HS-ESS1-4 : HS-ESS1-7
History of the Earth: HS-ESS1-5 : HS-ESS1-6 : HS-ESS2-1
Earth's Systems: HS-ESS2-2 : HS-ESS2-3 : HS-ESS2-5 : HS-ESS2-6 : HS-ESS2-7
Weather and Climate: HS-ESS2-4 : HS-ESS3-5 : HS-ESS2-8
Human Sustainability: HS-ESS3-1 : HS-ESS3-2 : HS-ESS3-3 : HS-ESS3-4 : HS.ESS3-6
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Earth and Space Science assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.