Cycling of Matter in the Earth's Interior (HS-ESS2-3): Develop a model based on evidence of Earth's interior to describe the cycling of matter by thermal convection
Develop a model based on evidence of Earth's interior to describe the cycling of matter by thermal convection involves understanding how heat drives the movement of materials within Earth. The Earth's interior is structured with a hot, solid inner core surrounded by a liquid outer core, which is in turn enveloped by the mantle and the crust. Thermal convection in the mantle, driven by the heat from the core, causes the semi-fluid mantle to circulate. Hot material rises towards the surface at mid-ocean ridges, cools, and then sinks back down in other regions, such as subduction zones. This convection process creates a cycle that moves and recycles matter within the Earth, driving the movement of tectonic plates and influencing geological processes such as volcanic activity and the formation of mountain ranges.
Main Concepts:
- The Earth's interior is composed of several layers, including the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin, outermost layer of the Earth, and it is composed of solid rock. The mantle is the largest layer and is composed of hot, semi-solid rock. The outer core is composed of liquid iron and nickel, while the inner core is a solid ball of iron and nickel.
- The Earth's interior is not static but undergoes constant movement and change. Convection currents in the mantle cause the tectonic plates to move, leading to earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Thermal convection is the process by which heat is transferred within the Earth's mantle. As hot material rises and cool material sinks, it creates convection currents that move the tectonic plates.
- One-dimensional and three-dimensional models of the Earth's interior are used to understand the structure and processes occurring within the Earth. These models use data from a variety of sources, such as seismic waves, to create images of the Earth's interior.
- Plate tectonics is the theory that explains how the Earth's crustal plates move and interact. It is based on the idea that the Earth's lithosphere is broken up into a number of plates that move relative to one another.
- Rocks and minerals can be identified and classified using various tests and protocols that determine their physical and chemical properties. These tests include hardness, color, luster, streak, and crystal structure.
- Evidence such as seismic waves, magnetic field records, and high-pressure laboratory experiments can be used to develop models of the Earth's interior. Seismic waves from earthquakes can be used to study the interior of the Earth, and magnetic field records can help identify the Earth's magnetic field reversal. High-pressure laboratory experiments can also simulate the conditions of the Earth's interior to study its properties.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
One of the pieces of evidence that Wegener was missing to explain his theory was the driving force for moving tectonic plates across Earth. The diagram below represents the structure of Earth and the geothermal gradient (the rate of change in temperature with respect to increasing depth in Earth’s interior). The model is a block diagram of a portion of Earth, with arrows representing the motion of tectonic plates.
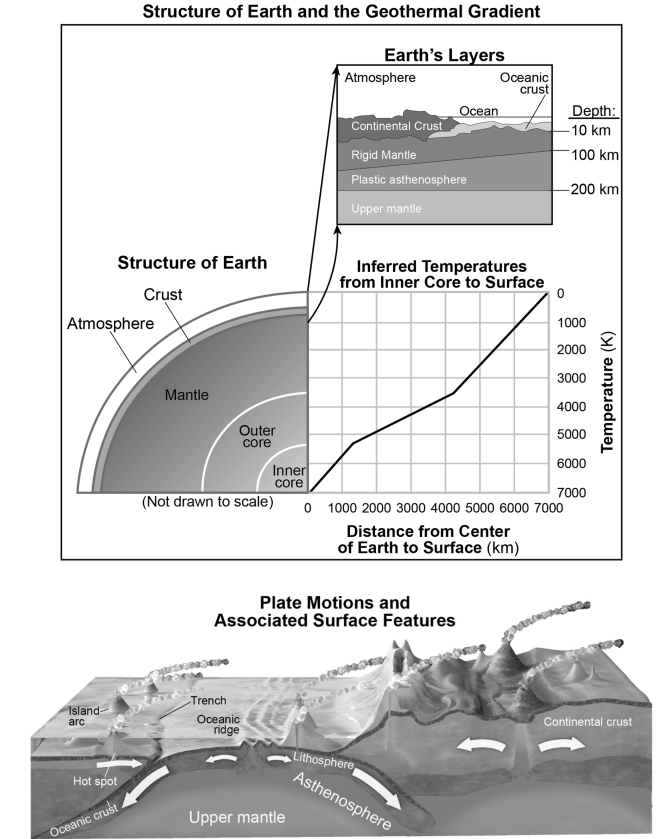
| Which statement, based on evidence presented in the diagram, model, and graph, most accurately identifies our current understanding of the driving force for the theory of plate tectonics? | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The highest amounts of heat from Earth’s core is cycled by thermal convection in the mantle, causing lithospheric plates to diverge at mid-ocean ridges. |
| 2 | The highest amounts of heat at Earth’s surface is cycled by thermal convection in the lithosphere, causing plates to diverge at hot spots. |
| 3 | Higher amounts of heat in the inner core than in the outer core transfer heat to the mantle, causing plates to diverge at ocean trenches. |
| 4 | Higher amounts of heat in the mantle than in the outer core transfer heat absorbed by the crust, causing plates to converge and form volcanic mountain chains on continents. |
General Question and Answer Section
- What are the four layers that make up the Earth's interior?
Answer: The crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. - What is thermal convection?
Answer: Thermal convection is the process by which heat is transferred within the Earth's mantle. - What is the difference between a one-dimensional and three-dimensional model of the Earth's interior?
Answer: A one-dimensional model considers the Earth's layers as radial layers determined by density, while a three-dimensional model takes into account mantle convection and the resulting plate tectonics. - What is plate tectonics?
Answer: Plate tectonics is the theory that explains how the Earth's crustal plates move and interact. - How are rocks and minerals identified and classified?
Answer: Rocks and minerals can be identified and classified using various tests and protocols that determine their physical and chemical properties. - What is seismic wave evidence, and how is it used to develop models of the Earth's interior?
Answer: Seismic wave evidence is the study of how waves generated by earthquakes propagate through the Earth. It can be used to determine the structure and composition of the Earth's interior. - What is magnetic field evidence, and how is it used to develop models of the Earth's interior?
Answer: Magnetic field evidence is the study of the Earth's magnetic field and its changes over time. It can be used to understand the processes occurring within the Earth's outer core. - What is high-pressure laboratory evidence, and how is it used to develop models of the Earth's interior?
Answer: High-pressure laboratory evidence involves conducting experiments on rocks and minerals under high-pressure conditions. It can be used to determine the composition and properties of the Earth's interior. - How does thermal convection contribute to plate tectonics?
Answer: Thermal convection drives the movement of the Earth's mantle, which in turn drives the movement of the crustal plates. - How do plate tectonics and the cycling of matter by thermal convection contribute to Earth's geological activity?
Answer: Plate tectonics and the cycling of matter by thermal convection cause geological activity such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
Space Systems: HS-ESS1-1 : HS-ESS1-2 : HS-ESS1-3 : HS-ESS1-4 : HS-ESS1-7
History of the Earth: HS-ESS1-5 : HS-ESS1-6 : HS-ESS2-1
Earth's Systems: HS-ESS2-2 : HS-ESS2-3 : HS-ESS2-5 : HS-ESS2-6 : HS-ESS2-7
Weather and Climate: HS-ESS2-4 : HS-ESS3-5 : HS-ESS2-8
Human Sustainability: HS-ESS3-1 : HS-ESS3-2 : HS-ESS3-3 : HS-ESS3-4 : HS.ESS3-6
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Earth and Space Science assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.