Feedback in Earth's Systems (HS-ESS2-2): Analyze geoscience data to make the claim that one change to Earth's surface can create feedbacks that cause changes to Earth's systems
Analyzing geoscience data reveals that a change to Earth's surface can trigger feedbacks that affect other Earth systems. For example, melting ice reduces the Earth's albedo (reflectivity), leading to increased absorption of sunlight and further warming, which in turn accelerates ice melt. Such feedback loops illustrate how interconnected Earth's systems are, where a change in one area, like surface conditions, can lead to significant and sometimes amplified impacts on climate, weather patterns, and ecosystems.
Main Concepts:
- Geoscience data is a collection of information about the Earth and its systems, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. Scientists use various tools and techniques to collect and analyze geoscience data, including remote sensing, geophysical surveys, drilling, and sampling. This data is essential to understanding Earth's systems and their interactions, which in turn helps to predict and mitigate natural hazards, manage resources, and make informed decisions about environmental policies.
- Feedback mechanisms are processes that amplify or dampen the effects of a particular factor on a system. In the context of Earth's systems, feedback mechanisms are important in understanding the cause-and-effect relationships between different systems. For example, if warming temperatures cause more ice to melt in the Arctic, the decreased albedo (reflectivity) of the exposed ocean water absorbs more heat, leading to further warming and more ice melt. This positive feedback loop can have significant impacts on global climate and sea levels.
- Climate feedbacks are the most well-known examples of feedback mechanisms that cause changes to Earth's systems. These feedbacks can be positive or negative and can occur within individual systems or between systems. For example, warming temperatures can cause permafrost to thaw, releasing large amounts of methane into the atmosphere, which can further increase global temperatures. Loss of ground vegetation, dammed rivers, and loss of wetlands are other examples of feedback mechanisms that can have significant impacts on Earth's systems. For example, when forests are cleared, the loss of vegetation can lead to soil erosion, which in turn can cause changes in river channels, sediment deposition, and nutrient cycling.
- Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and urbanization, have a significant impact on Earth's systems and can cause severe changes in the environment. These changes can affect climate, water availability, soil quality, and biodiversity. For example, burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and contribute to global warming. Deforestation can lead to soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and changes in local climate patterns. Urbanization can cause changes in land use, water availability, and air quality, affecting both human health and ecosystems.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
The maps below show the distribution of continents 130 Ma (million years ago) to the present day. Water flux is the amount of water flowing into Earth’s mantle at subduction zones. White subduction zones indicate less relative water flux while black subduction zones indicate a greater water flux relative to white.
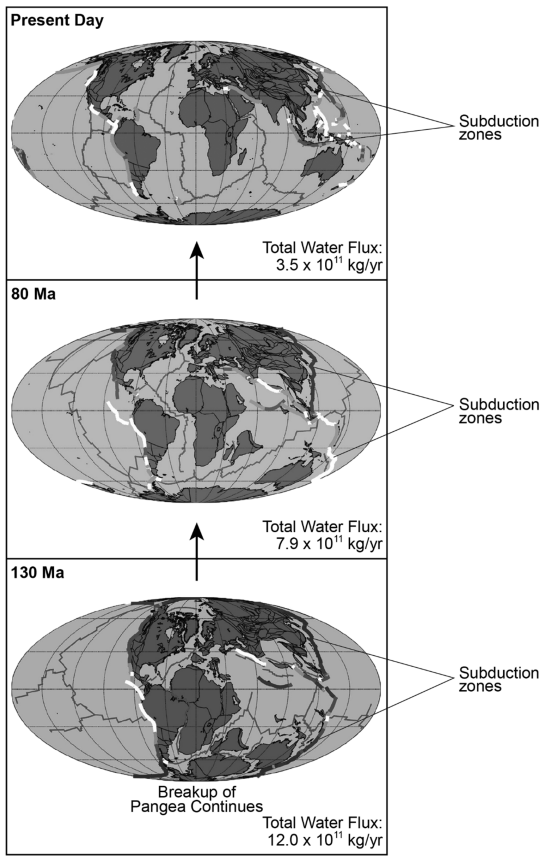
| After Pangea broke up 130 Ma, over time the number of subduction zones on Earth changed. This change to the geosphere created a feedback that caused changes to Earth’s hydrosphere. Use the geoscience information provided on the maps to make a prediction about how the hydrosphere most likely changed and how this change most likely affected the global sea level. Predicted hydrosphere change: ________________________ Predicted sea level change: ________________________ |
|
|---|---|
Predicted hydrosphere change:
— Less water flowed into Earth’s mantle.
— Less water flowed into the mantle, while more water stayed on the surface.
Predicted sea level change:
— sea level increased
— Sea level must have increased because there was less water on the surface.
General Question and Answer Section
- Why is analyzing geoscience data important?
Answer: Analyzing geoscience data is essential to understand Earth's systems and their interactions. - What are feedback mechanisms, and why are they important?
Answer: Feedback mechanisms are important in understanding the cause-and-effect relationship between different Earth's systems. - What are the examples of climate feedbacks?
Answer: Climate feedbacks include how an increase in greenhouse gases causes a rise in global temperatures that melts glacial ice, which reduces the amount of sunlight reflected from Earth's surface, increasing surface temperatures and further reducing the amount of ice. - How does the loss of ground vegetation cause changes to Earth's systems?
Answer: The loss of ground vegetation causes an increase in water runoff and soil erosion. - What is the impact of dammed rivers on Earth's systems?
Answer: Dammed rivers increase groundwater recharge, decrease sediment transport, and increase coastal erosion. - How does the loss of wetlands cause changes to Earth's systems?
Answer: The loss of wetlands causes a decrease in local humidity that further reduces the wetland extent. - What is the impact of human activities on Earth's systems?
Answer: Human activities have a significant impact on Earth's systems and can cause severe changes in the environment. - What are the examples of human activities that cause changes in Earth's systems?
Answer: Examples of human activities that cause changes in Earth's systems include deforestation, industrialization, and pollution. - What is the role of humans in mitigating the impact of human activities on Earth's systems?
Answer: Humans can reduce the impact of their activities on Earth's systems by adopting sustainable practices, reducing pollution, and conserving natural resources. - Why is it essential to understand the feedback mechanisms in Earth's systems?
Answer: Understanding the feedback mechanisms in Earth's systems is crucial to predict and mitigate the impact of human activities on the environment.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
Space Systems: HS-ESS1-1 : HS-ESS1-2 : HS-ESS1-3 : HS-ESS1-4 : HS-ESS1-7
History of the Earth: HS-ESS1-5 : HS-ESS1-6 : HS-ESS2-1
Earth's Systems: HS-ESS2-2 : HS-ESS2-3 : HS-ESS2-5 : HS-ESS2-6 : HS-ESS2-7
Weather and Climate: HS-ESS2-4 : HS-ESS3-5 : HS-ESS2-8
Human Sustainability: HS-ESS3-1 : HS-ESS3-2 : HS-ESS3-3 : HS-ESS3-4 : HS.ESS3-6
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Earth and Space Science assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.