HS-ESS2-1: Develop a model to illustrate how Earth's internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and ocean-floor features
Developing a model to illustrate how Earth's internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and ocean-floor features involves understanding the dynamic interactions between Earth's internal forces and surface activities. Internal processes like volcanic activity, earthquakes, and plate tectonics shape large-scale features such as mountain ranges, ocean basins, and continental shelves over millions of years. Meanwhile, surface processes like weathering, erosion, and sedimentation gradually alter the landscape at smaller scales and over shorter timeframes. These processes work together across varying spatial and temporal scales to continuously reshape Earth's surface, leading to the formation and evolution of continental and ocean-floor features.
Main Concepts:
- The Earth is a dynamic planet, and its internal and surface processes occur at different spatial and temporal scales. The internal processes occur over millions of years and involve tectonic activity, mantle convection, and volcanic activity, while surface processes operate over much shorter timeframes, typically over thousands of years, and include weathering, erosion, and deposition.
- Constructive processes refer to the activities that build or create new landforms or features on the Earth's surface. Volcanism involves the eruption of magma onto the surface, forming new landforms such as volcanoes and lava fields. Tectonic uplift refers to the rising of the Earth's crust, forming mountains, plateaus, and other highland areas. Deposition is the process of accumulating sediment and debris in a specific location, resulting in the formation of new landforms such as deltas and beaches.
- Destructive processes refer to the activities that break down or remove existing landforms or features. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces, and it can occur through mechanical, chemical, or biological means. Subduction occurs when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, leading to the destruction of the descending plate and the formation of mountain ranges. Coastal erosion refers to the process of the removal of sediment and rock by the action of waves and currents.
- Constructive processes such as tectonic uplift, volcanic activity, and deposition can create land features such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus. Tectonic uplift results in the formation of mountains, while volcanic activity can lead to the formation of volcanic mountains and plateaus. Deposition can lead to the formation of valleys, canyons, and other landforms.
- Sea-floor features such as trenches, ridges, and seamounts are also a result of constructive processes. Mid-ocean ridges form where tectonic plates are moving apart, leading to the creation of new sea-floor crust. Trenches form where tectonic plates are moving towards each other, resulting in the subduction of one plate beneath another. Seamounts are volcanic mountains that form on the sea floor.
- Weathering and coastal erosion are examples of destructive processes that shape the Earth's surface. Weathering can create new landforms, such as caves and arches, while coastal erosion can lead to the formation of cliffs and other coastal landforms.
- The formation of land and sea-floor features is a result of the interplay between constructive and destructive processes. The Earth's surface is constantly changing as a result of these processes, leading to the formation of new landforms and the destruction of existing ones. The balance between these processes determines the nature and extent of the changes that occur over time.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener was a German geophysicist and meteorologist who proposed the theory of continental drift in 1912. This theory attempted to explain how similar rock formations and plant and animal fossils could be found on separate continents. Widely dismissed by other scientists from Wegener’s time, continental drift would eventually be accepted and become known as the theory of plate tectonics by the 1960s. The model below shows some information about the position of the continents.
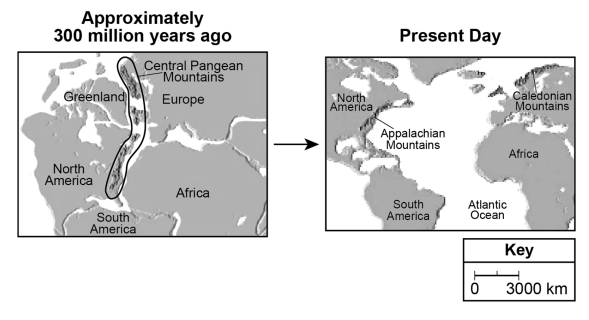
| Use the model to explain how the Central Pangean Mountains were separated into the Appalachian Mountains and the Caledonian Mountains. In your explanation, include a spatial or a temporal numerical value in which this process occurred. | |
|---|---|
— Over 300 million years, the continents separated by diverging tectonic plates.
— Diverging plates separated the continents, creating two separate mountain chains located thousands of kilometers apart/~5000 - 7000 km apart
General Question and Answer Section
- What are constructive processes?
Answer: Constructive processes are processes that create or build up land features or sea-floor features, such as volcanism, tectonic uplift, and deposition. - What are destructive processes?
Answer: Destructive processes are processes that wear down or erode land features or sea-floor features, such as weathering, subduction, and coastal erosion. - What are some examples of land features created by constructive processes?
Answer: Mountains, valleys, and plateaus are examples of land features created by constructive processes. - What are some examples of sea-floor features created by constructive processes?
Answer: Trenches, ridges, and seamounts are examples of sea-floor features created by constructive processes. - How do destructive processes shape the Earth's surface?
Answer: Destructive processes such as weathering and coastal erosion wear down or erode land features or sea-floor features, changing their shape and size. - What is the interplay between constructive and destructive processes?
Answer: The interplay between constructive and destructive processes results in the formation of land and sea-floor features. - How do volcanism and tectonic uplift create land features?
Answer: Volcanism and tectonic uplift create land features by building up the Earth's surface through the deposition of volcanic material and the uplifting of tectonic plates. - How does subduction create destructive processes?
Answer: Subduction creates destructive processes by pulling down and eroding the edge of a tectonic plate as it sinks beneath another plate. - What is the role of deposition in the formation of land features?
Answer: Deposition is the process of laying down sediment, rock, or other materials, and can create land features such as deltas, alluvial fans, and sand dunes. - How does coastal erosion shape the Earth's surface?
Answer: Coastal erosion wears down and erodes the edges of land masses, resulting in the formation of features such as cliffs, sea stacks, and beaches.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
Space Systems: HS-ESS1-1 : HS-ESS1-2 : HS-ESS1-3 : HS-ESS1-4 : HS-ESS1-7
History of the Earth: HS-ESS1-5 : HS-ESS1-6 : HS-ESS2-1
Earth's Systems: HS-ESS2-2 : HS-ESS2-3 : HS-ESS2-5 : HS-ESS2-6 : HS-ESS2-7
Weather and Climate: HS-ESS2-4 : HS-ESS3-5 : HS-ESS2-8
Human Sustainability: HS-ESS3-1 : HS-ESS3-2 : HS-ESS3-3 : HS-ESS3-4 : HS.ESS3-6
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Earth and Space Science assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.